Machine learning software represents a fundamental advancement in terms of the applications that IT can be applied against, but the number of use cases for those applications has been limited to scenarios where the underlying data has been fairly structured.
Skytree is moving to expand the use cases for machine learning software into the realm of unstructured data with the release today of version 15.2 of its namesake machine learning software.
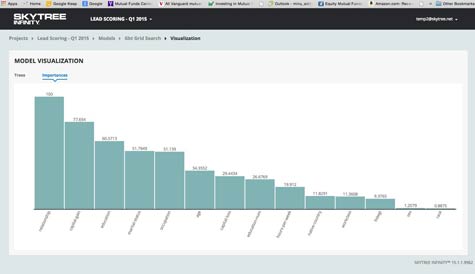
While machine learning algorithms are often opaque, Robert Dutcher, vice president of marketing for Skytree, said that with this release, the company is adding support for variable importance, which enables data scientists to visually see how important each variable is in making a specific prediction. The graphical tool not only makes it easier to fine tune the model the machine learning algorithms create, it also creates a mechanism through which the validity of that prediction can be more easily validated, said Dutcher.
Dutcher said that Skytree is trying to make machine learning algorithms more accessible using a console that enables data scientists to more easily peruse a library of those algorithms. The end goal is to make it simple for even “citizen data scientists” to build a model that can be easily adjusted using those algorithms, said Dutcher.
Just how widely machine learning software will be deployed throughout the enterprise remains to be seen, but as these algorithms become more widely available, the sophistication of the models that can be created will increase substantially. It’s less clear what impact those algorithms will have, but at the moment, many businesses are engaged in something of an algorithm arms race to make sure they don’t wind up on the losing end of a machine learning application with a competitive advantage they simply can’t match.